Connectivity, integration and technology development
Connecting EVs
EVs represent a new technology and their electric and digital nature allows them to be better integrated into collateral systems such as the digital world, the energy sector and other infrastructure. Therefore, organisations with EV fleets will be able to tap into a new array of business opportunities such as smart charging and vehicle-to-grid. When considering a technological outlook, electric vehicles will allow for an easier transition to other mobility technologies, such as vehicle automation (as automated vehicles are inherently electric). You can read more in the Future of mobility article.
Vehicle to grid (V2G)
V2G refers to the ability of bi-directional communication between an electric vehicle and an Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment, which allows for an EV to be charged and discharged into the power grid. V2G directs the charging and discharging of electric-vehicle batteries in accordance with users’ needs and the grid’s supply of available electricity. When electricity supply exceeds demand (notably during peak periods of renewable energy production), charging occurs at the maximum level; however, during peak electricity demand, vehicles can then supply electricity into the grid. V2G therefore allows the electricity grid to optimise the supply of local renewable energy and reduce infrastructure costs, while customers can enjoy greener, more economical consumption of electricity and be financially rewarded for serving the electricity grid. [4] V2G has a demonstrated revenue of €1,869/year per vehicle in Denmark [3] and with a global estimated value of US $ 2 billion by 2025. [1] There are more than 50 projects internationally testing different elements of V2G, including fully commercial applications in the US. The figure below shows four models of V2G [2] and the potential electricity and revenue flows across its stakeholders.
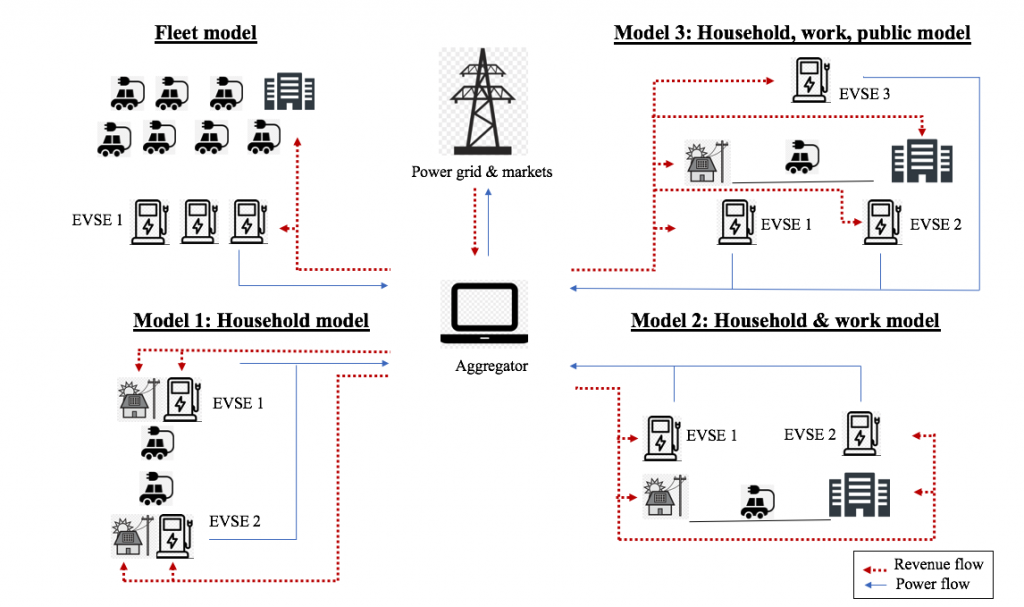 Source: Noel, L., Zarazua de Rubens, G., Kester, J., Sovacool, B., 2019
Source: Noel, L., Zarazua de Rubens, G., Kester, J., Sovacool, B., 2019
Digitalisation & customisation
EVs are digitally connected. This can open an array of services and opportunities: from trip planning based on available charging stations, to connectivity with other devices and infrastructure, to the customisation of the driving experience. Vehicle manufacturers are creating intelligent remote control systems, through smartphone apps, that allow for customised driving performance to optimise range. [3]


